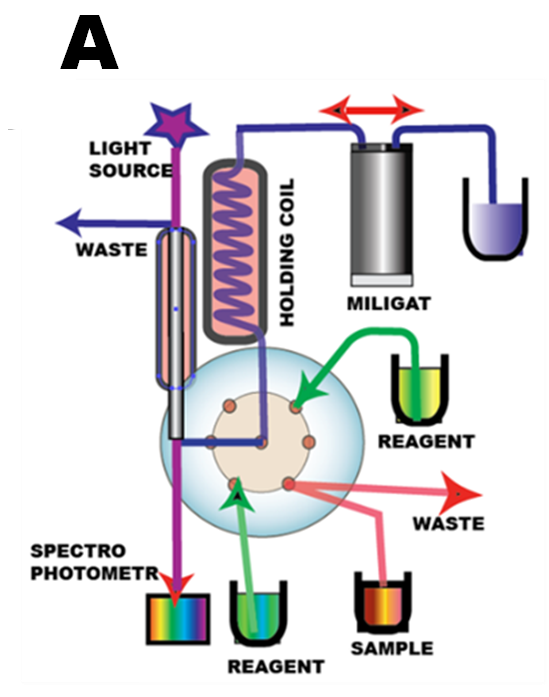
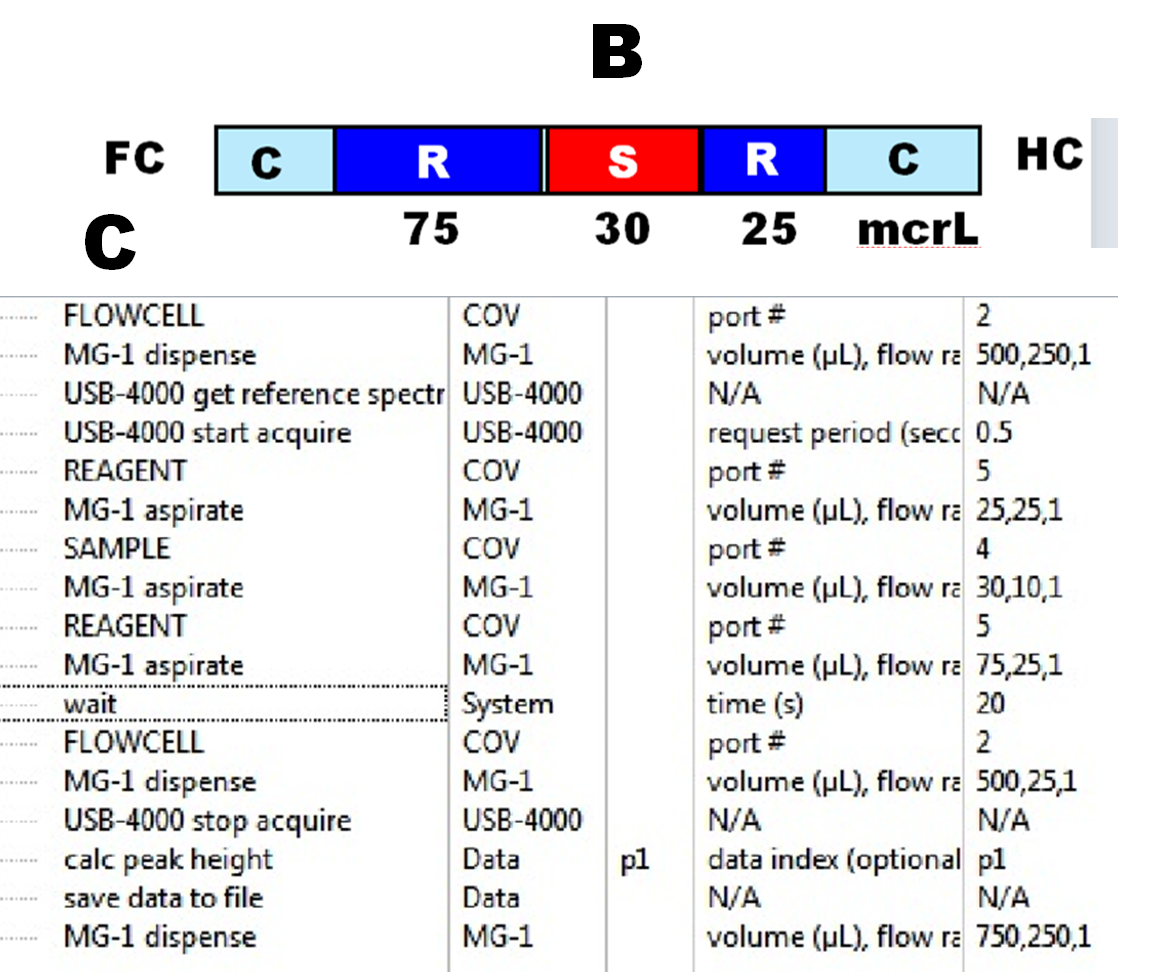
There are three ways in which an enzymatic assay can be carried out, depending on, where in the flow system the conversion of the target analyte will take place:
- stopping flow in the holding coil (SHC) for end point measurement
- stopping flow in the flow cell (SFC) for end point measurement
- stopping flow in the flow cell (SFC) for reaction rate measurement
The SHC method offers highest sampling frequency, but SFC method based on reaction rate measurement is more selective, since it eliminates the background color of reagents and real life samples.
The apparatus is configured as single line system (miniSIA-1) furnished with thermostated holding coil and thermostated 15cm long flowcell. (A) As a model reaction the widely used assay of glucose based on glucose oxidase with spectrophotometric detection is used here to compare the three approaches mentioned above. Oxidation of glucose to gluconate and hydrogen peroxide is quantified trough production or red quinoeimine dye (Trinder, 1969).
Methodology of Enzymatic Assays
1 to 600ppM Glucose
2.2.10.
The commercially available reagent comprising glucose oxidase, proxidase, color reagent and buffer combined (Pointe Scientific), was diluted 1:5 with DI water prior to use. DI water was also used as a carrier and the sandwich SIA sequence (B) was used in all experiments.
The SHC assay protocol (C) was used to explore kinetics of the assay at room and at elevated temperature (next page) and for development of calibration curve.
The reason for diluting the reagent with DI water (1:5) was to reduce reagent blank and to promote mixing by using 75 mcrL of second reagent zone. Note that only 20 mcrL of supplied undiluted reagent was used for each measurement, compared to 3 mL suggested by manufacturer.
P. Trinder, Ann.Clin.Biochem.6:24 (1969)
Pointe Scientific 5449 Research Drive Canton MI48188 USA Liquid Glucose Oxidase Reagent Set